 Voltage Fluctuations are quite common in most places in India. No wonder we at Bijli Bachao get so many questions on our page for voltage stabilisers: working, sizing and power consumption. The biggest concern that people have is that voltage fluctuations can harm their appliances. This is true to a great extent for some appliances. But people hardly consider the impact of voltage fluctuations on electricity consumption. In this article we will not only cover the impact of voltage fluctuations on appliances but will also tell you about its impact on power consumption of various appliances.
Voltage Fluctuations are quite common in most places in India. No wonder we at Bijli Bachao get so many questions on our page for voltage stabilisers: working, sizing and power consumption. The biggest concern that people have is that voltage fluctuations can harm their appliances. This is true to a great extent for some appliances. But people hardly consider the impact of voltage fluctuations on electricity consumption. In this article we will not only cover the impact of voltage fluctuations on appliances but will also tell you about its impact on power consumption of various appliances.
Standard input voltage in India
In India, electricity distribution is at 230V for single phase and 415 V for three phase. In a three phase connection, the connection is divided into 3 lines each of 230 V. All appliances sold in India work in the range of 220-240 V. Voltage lower and higher than this range needs to be corrected if the appliance cannot handle that voltage. Voltages at many places in India go down to 150-160 V on a regular basis.
Two types of appliances
Different type of appliances have different behaviour on voltage fluctuations. And if you are planning to put a voltage stabiliser, you need to work accordingly.
There are two kinds of appliances: 1) Without Motor (resistive load) and 2) With Motor (inductive load).
Appliances without motor include:
- Luminaire like Bulbs/Tube lights/CFLs.
- Heaters like water heaters and room heaters.
- Electronics like Televisions/Music Systems/DVD/Home Theatre/ Laptops/Phones.
Appliances with motor include:
- Air Conditioners
- Refrigerators
- Ceiling Fans
- Mixer Grinders
- Pumps
- Washing Machines
Appliances without motors (resistive load) and their behaviour on voltage fluctuations
Appliances like luminaire (bulbs, tube lights and CFLs) and heaters (like room heaters and water heaters) do not need voltage stabilisers. When the voltage is less, less current flows through them. When voltage is more, more current will flow through them. So when voltage is less, the output of these appliances will be less or the bulb will give less light, room heater will heat less, water heater will heat slowly. And as the bulb will give lesser light the power consumption of the bulb will be less. In fact many municipalities reduce the voltage of street lights at times when the light requirement is less to reduce the power consumption of the bulbs. However when the voltage is higher than normal, more current will flow through these appliances. And if the high voltage is consistent, and thus the high current is consistent, it may result in burning of the bulb or the appliance. If it does not burn, it will consume more electricity.
Most electronics like TVs, DVD players, etc do not work at 230 V. These appliances have an internal device called SMPS (Switch Mode Power Supply) which converts incoming 230 V to 12V or 24V (whichever is required by the appliance). Thus none of the electronic appliances need voltage stabilisers. I repeat, electronic appliances do not need voltage stabilisers. They are neither impacted by high voltage, nor by low voltage. So electronic devices do not need any protection. There are products available in market because people feel the need of protecting their appliances, but these devices do not need any protection. The power consumption of electronic products does not change with voltage fluctuations. Also, their output does not change.
What is power surge?
Power surge or spike is fast, short sudden increase in voltage and current that can cause damage to sensitive electronics. It typically happens when there is short circuit or there is lightening/thunderstorm. A surge protector or spike guard that is available in local market can protect against short circuit, but there is nothing available in the market that can protect electronics from power surges during lightening. However the main thing that gets damaged during a power surge is the SMPS. So for e.g. in case of laptop, the laptop charger is the one that will get damaged in case of power surge. The laptop will still be safe. Similarly in TV only the power circuit will get damaged and not any other part. The best protection from power surges due to lightening is to switch off the TV from main supply during that period.
Appliances with motors (inductive load) and their behaviour on voltage fluctuations
All appliances with motors have an operating voltage range. Appliance like a ceiling fan have much larger operating voltage range and thus they are able to work even at lower voltages. But appliances like air conditioners have very small operating voltage range and thus they do not work at low voltages. If the voltage provided to them is lower than their operating voltage range, then either they will not start at all, and if they are already running, they will start producing a humming sound. This humming sound happens as these motors draw more current to run the system. This can lead to over heating and burning of the motor if persistent. Thus saving induction motors from voltage fluctuations is very important.
At high voltages these appliances draw more current only at the time of starting, but once they reach steady state the current is much less. But still the high starting current can damage the system and thus appliances with motors need to be protected both from high as well as low voltages. So you do need to put voltage stabiliser to protect these appliances. However before putting a voltage stabiliser, it is very important to find the operating voltage range of the appliance and the fluctuations that happen in your area. For e.g several refrigerator models available in market these days have large operating voltage range and thus these models do not need voltage stabilisers (unless your voltage goes below the operating range).
As far as power consumption of appliances with motors is concerned, it depends on the voltage as well as the load on the machine. Typically if the load is less than efficiency of the motor is less at standard voltage. For example, if your room need 0.5 tons cooling and you put 1.5 ton AC, efficiency will be lower but you get the advantage of quick cooling. If your washing machine can handle 7 kg load and you have put just 2 kg, then its efficiency will be low. This is because you are using more energy to do small work. However at lower load if the voltage is less, the efficiency improves. So if you know that your AC is oversized and input voltage in your house is 200 V or 210V then energy consumption will be lower.
At full load high voltage is beneficial for motors as their efficiency increases. Here is what Bureau of Energy Efficiency mentions for inductive loads: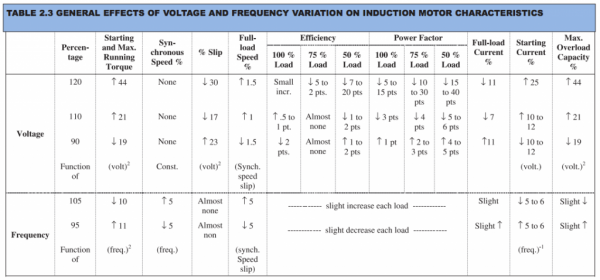
Conclusion
We receive several questions from people asking for voltage stabilisers for various appliances. Please note that for luminaries and electronics, there is no need of putting a voltage stabiliser. However if you want to protect an appliance that has motor (or compressor), then you do need to protect it from both high as well as low voltages. And you do need a voltage stabiliser for it.
As far as electricity consumption is concerned, low voltages reduces electricity consumption whereas high voltages can increase your electricity consumption. If it is just slightly low consistently (say about 210V), then it is good for you or if it is slightly high (say about 240V) then it will increase your electricity consumption. But if the voltage is consistently lower than 190V or higher than 250-260V, then you should lodge a complaint with your electricity distribution company as it can damage some of your appliances.
Also please note that voltage stabilisers have their own electricity losses which depend on size of the stabiliser. A stabiliser will typically have 3-4% losses and thus never oversize the stabiliser. A 3 kVA stabiliser will have 3% losses on 3 kVA even if you are running just 1 kVA load on it. So if you have 1 kVA load then put 1 kVA stabiliser for it. Also, look for the appliances which has high voltage range, because that will save you from buying a voltage stabiliser and certainly saving on electricity too. Also make sure that if you have a voltage stabiliser, you switch it off from mains as even if the appliance is not used and stabiliser is on, it will loose 1% electricity consistently. So if you have a 1 kVA stabiliser on an air conditioner it will loose about 0.15 units of electricity in an hour even if AC is not used.







